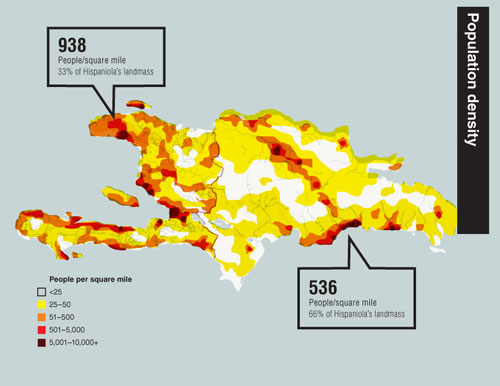
Service Quality:
-despite strong efforts and continued government support, quality and continuity are inadequate in the Dominican Republic
-scarcity increasing because of excessive consumption in urban areas
- only about 10.5% of the population connected to the water system receive water on a continuous basis
-many people living under the poverty line cannot afford to pay for water
Services
|
By System
|
By Service Population
|
Continuous
|
40%
|
10.5%
|
Inadequate
|
60%
|
89.9%
|
Drinking Water Quality:
-there are often poor conditions at the purification systems
-38.4% of systems have no chlorination filter installed
-a major effect is the high rates of Cholera throughout the country
Problems:
-government has been trying to improve the water systems but very expensive
-there is no specific government agency in charge or water or sanitation
Recommendations:
Suggestions
-put in rain barrels to catch the rain and use as drinking water
-work to create cleaner and safer purification systems in larger cities
-truck water out to people living under the poverty line for lower price
-use rain water for agriculture
-although my suggestions would be costly, it would save lives
-because my suggestion is to only fix the purification systems in large cities it would save money
-that money can be used to purchase water basins and truck water out to people
-with these rain basins that water caught can be used for agriculture
Waste water Treatment:
-about 49% of waste water is collected and receives some kind of treatment
-insufficient treatment
Major Projects:
- the Interamerican Development Bank is partnering with Hazen and Sawyer to create a sanitary sewage master plan for Santo Domingo
-will treat waste water collection, treatment and disposal

Solid Waste Disposal:
-solid waste is not being disposed of properly
-direct correlation between inadequate disposal of solid waste and sickness
-the waste is not being recycled or sorted
-being put into streams and landfills
-not regulated at all
-piling up and creating pollution for nearby neighborhoods and cities
-because clean water is such an issue, solid waste disposal is not the major concern
Major Projects:
-a 5 million dollar project is currently being worked on to put in a recycling center and to create a safe solid waste disposal center
Recommendation:
-to implement recycling to help reduce the amount of waste going into landfills and proceed to dispose of this waste properly separating any chemical products or toxic waste
-although my solution would be very costly it would benefit in the future and would reduce the amount of sickness from poor solid waste disposal

Air Pollution:
-MAJOR issue
-many companies came over and set up factories and disregarded environmental standards
-Blacksmith Institute set up many factories in Bajos de Haina disregarding all environmental stands and now Bajos de Haina is considered in the top 10 most polluted places on Earth
-many high levels of lead and other chemicals
-extremely dangerous to live there, many health problems
-overall the air quality is very poor
-in certain areas it is worse
Policies:
-to use more alternative energy
-building wind turbines and installing solar panels
-trying to make factories cleaner(coal brushes)
Water Pollution:
-water is not safe to drink in the Dominican Republic
-pollution is mainly from depletion of groundwater and unregulated solid waste disposal
-poor purification systems make this pollution irreversible
-better purification systems are being put in place to improve quality of water

Analysis:
-I think the worst pollution problem facing the Dominican Republic is the poor quality and scarcity of drinking water. With purification systems lacking important steps in the purification process, such as chlorination, the water is not considered safe to drink. Even though the water is not considered safe, it is the only water being provided for the people, therefore they drink it and get sick. Being that there is a direct correlation between unsafe drinking water and illness I think this is the most important pollution problem facing the Dominican Republic.